How do die-cut components help in thermal management?
September 11 '21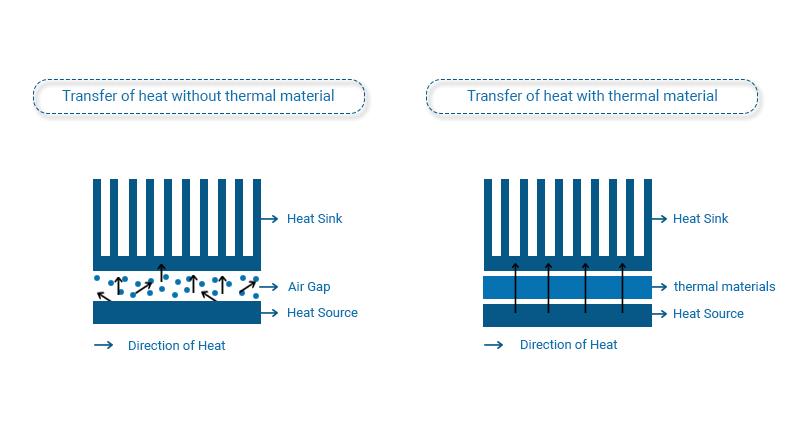
As electronic devices and equipment become smaller, engineers and designers face a range of new challenges. One of them concerns the dissipation of heat.
Every electronic device emits heat. If its manufacturer fails to add a proper heat outlet, the internal temperature of the device might rise, causing poor performance, failure, or damage to its important components.
How can engineers reduce the temperature of the device? This is where heat dissipation comes in. The idea is to move the heat from its source to a heat sink – which can be an air duct or vent. By using thermal interface materials (TIM), engineers can address this problem.
Keep on reading to find out how die-cut components help in the thermal management of equipment used across all industries.
What are thermal interface materials?
TIM are materials that facilitate the transfer of heat away from its source. They are integrated with devices at various stages of product development.
To understand how thermal interface materials work, we need to start with the concept of thermal conductivity. We measure thermal conductivity in watts per square meter of surface area. The temperature gradient is one Kelvin per meter of the thickness (W/m-k).
When an integrated circuit (IC) in a device heats up, a thermal material can drive that heat in a vertical direction so that it gets away from the source. We use the measure of W/m-k to understand how fast heat is transferred from the circuit to the heat sink.
If the thermal material fails to form a close bond with the IC, you can expect air bubbles will form. The resistance of such air bubbles can delay or stop heat transmission. When it comes to selecting the best thermal material for specific applications, having a firm grasp over conductivity and impedance is essential.

Benefits of thermal interface materials
These materials are extremely soft and are used to fill the gap between the different components in a piece of equipment. The idea is to create more contact points, which allows directing the heat more efficiently.
Key benefits of thermal interface materials include:
- Improved thermal coupling between the source of heat and heat sink,
- Excellent conformability to substrates that have an uneven and irregular structure,
- Fast and easy application,
- Greater device durability and performance.
Examples of thermal interface materials
The two most commonly used die-cut components that serve as thermal interface materials are thermal pads and thermal tapes. Let’s take a closer look at both these components to discover their unique advantages.
Thermal pads
Thermal pads are soft thermal conductive interface pads that offer a close bond between the IC and the heat sink, reducing the resistance to nearly zero. Thermal pads flow into all the nooks present between the heat sink and IC. The goal is to provide a high degree of “wet out” for more efficient heat transfer.
Thermal pads are available in a variety of thermal conductivities and softness grades – they work great for filling in the gaps.
We can differentiate between two types of thermal pads.
Silicone thermal pads
Despite their tendency to outgas, silicone thermal pads are commonly used in a variety of applications – from portable devices and memory modules to telecommunications hardware, laptops and desktop computers, and flat panel displays.
Key features:
- The thermal conductivity range is up to 8.0 W/m-k
- Possible thickness range: 0.25 to 5mm
Non-silicone thermal pads
Non-silicone thermal pads are made of acrylic materials and have the same properties as silicone pads. They’re a great alternative to silicone pads since they don’t outgas or cause fogging on a lens. That’s why lenses for cameras are among the top applications of non-silicone thermal pads
Key features:
- Thermal conductivity range of up to 7.8 W/m-k
- Thickness range: 0.16 to 0.4mm
Thermal conductive tapes
Acrylic adhesives with highly conductive ceramic particles are the foundation of thermal conductive tapes. While thermal pads fill the space between the IC and the heat sink, the latter eventually needs to be fastened to the PCBs.
This is where conductive tapes come in. You can use them to bond the IC and heat sink without any mechanical fasteners. Heat sinks, spreaders, and other cooling devices can be easily bonded to IC packages and power transistors with the help of these thin tapes characterized by high stickiness.
Note that the tapes come with a modest thermal conductivity (about 0.6 W/m-k). Such a low heat transfer might not work for all applications, but it’s just perfect for low-temperature LEDs.
Key features:
- Thermal conductivity range of up to 0.6 W/m-k
- Thickness range: 2 to 20 mils
Get quality die-cut components at Melrose
Our engineers have decades of experience in providing companies across the most demanding sectors with high-quality die-cut components. Completement your application with components that help to dissipate heat and ensure excellent performance and durability of your device. Contact our consultants to take the next step in your product design.
